[Python] Градиентный спуск в Python
Автор
Сообщение
news_bot ®
Стаж: 7 лет 10 месяцев
Сообщений: 27286

Задача и требования
- Основная цель - создать алгоритм, который найдет максимальное значение по модулю минимума на заданном радиусе.
- Алгоритм должен быть эффективным и работать достаточно быстро
- Результат должен быть отображен на графике
Введение, описание алгоритмаРабочая область функции (заданный интервал) разбита на несколько точек. Выбраны точки локальных минимумов. После этого все координаты передаются функции в качестве аргументов и выбирается аргумент, дающий наименьшее значение. Затем применяется метод градиентного спуска.РеализацияПрежде всего, numpy необходим для функций sinus, cosinus и exp. Также необходимо добавить matplotlib для построения графиков.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
Константы
radius = 8 # working plane radius
centre = (global_epsilon, global_epsilon) # centre of the working circle
arr_shape = 100 # number of points processed / 360
step = radius / arr_shape # step between two points
arr_shape должна быть 100, потому что, если она больше, программа начинает работать значительно медленнее. И не может быть меньше, иначе это испортит расчеты.Функция, для которой рассчитывается минимум:
def differentiable_function(x, y):
return np.sin(x) * np.exp((1 - np.cos(y)) ** 2) + \
np.cos(y) * np.exp((1 - np.sin(x)) ** 2) + (x - y) ** 2
Затем выбирается приращение аргумента:
Поскольку предел аргумента стремится к нулю, точность должна быть небольшой по сравнению с радиусом рабочей плоскости:
global_epsilon = 0.000000001 # argument increment for derivative
Для дальнейшего разбиения плоскости необходим поворот вектора: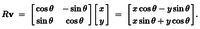
Если вращение применяется к вектору (x, 0), повернутый вектор будет вычисляться следующим образом:
def rotate_vector(length, a):
return length * np.cos(a), length * np.sin(a)
Расчет производной по оси Y, где эпсилон - значение y:
def derivative_y(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(arg, epsilon + global_epsilon) -
differentiable_function(arg, epsilon)) / global_epsilon
Вычисление производной по оси X, где эпсилон - значение x:
def derivative_x(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(global_epsilon + epsilon, arg) -
differentiable_function(epsilon, arg)) / global_epsilon
Расчет градиента:
Поскольку градиент вычисляется для 2D-функции, k равно нулю
gradient = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x)
Схема генерации точек
Возвращаемое значение представляет собой массив приблизительных локальных минимумов.Локальный минимум распознается по смене знака производной с минуса на плюс. Подробнее об этом здесь: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxima_and_minima
def calculate_flip_points():
flip_points = np.array([0, 0])
points = np.zeros((360, arr_shape), dtype=bool)
cx, cy = centre
for i in range(arr_shape):
for alpha in range(360):
x, y = rotate_vector(step, alpha)
x = x * i + cx
y = y * i + cy
points[alpha][i] = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x) > 0
if not points[alpha][i - 1] and points[alpha][i]:
flip_points = np.vstack((flip_points, np.array([alpha, i - 1])))
return flip_points
Выбор точки из flip_points, значение функции от которой минимально:
def pick_estimates(positions):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[1][0])
cx, cy = centre
best_x, best_y = cx + vx * positions[1][1], cy + vy * positions[1][1]
for index in range(2, len(positions)):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[index][0])
x, y = cx + vx * positions[index][1], cy + vy * positions[index][1]
if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y):
best_x = x
best_y = y
for index in range(360):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, index)
x, y = cx + vx * (arr_shape - 1), cy + vy * (arr_shape - 1)
if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y):
best_x = x
best_y = y
return best_x, best_y
Метод градиентного спуска:
def gradient_descent(best_estimates, is_x):
derivative = derivative_x if is_x else derivative_y
best_x, best_y = best_estimates
descent_step = step
value = derivative(best_y, best_x)
while abs(value) > global_epsilon:
descent_step *= 0.95
best_y = best_y - descent_step \
if derivative(best_y, best_x) > 0 else best_y + descent_step
value = derivative(best_y, best_x)
return best_y, best_x
Нахождение точки минимума:
def find_minimum():
return gradient_descent(gradient_descent(pick_estimates(calculate_flip_points()), False), True)
Формирование сетки точек для построения:
def get_grid(grid_step):
samples = np.arange(-radius, radius, grid_step)
x, y = np.meshgrid(samples, samples)
return x, y, differentiable_function(x, y)
Построение графика:
def draw_chart(point, grid):
point_x, point_y, point_z = point
grid_x, grid_y, grid_z = grid
plot.rcParams.update({
'figure.figsize': (4, 4),
'figure.dpi': 200,
'xtick.labelsize': 4,
'ytick.labelsize': 4
})
ax = plot.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(point_x, point_y, point_z, color='red')
ax.plot_surface(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, rstride=5, cstride=5, alpha=0.7)
plot.show()
Функция main:
if __name__ == '__main__':
min_x, min_y = find_minimum()
minimum = (min_x, min_y, differentiable_function(min_x, min_y))
draw_chart(minimum, get_grid(0.05))
График: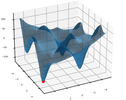
ЗаключениеПроцесс вычисления минимального значения с помощью алгоритма может быть не очень точным при вычислениях в более крупном масштабе, например, если радиус рабочей плоскости равен 1000, но он очень быстрый по сравнению с точным. Плюс в любом случае, если радиус большой, результат находится примерно в том положении, в котором он должен быть, поэтому разница не будет заметна на графике.Исходный код:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
radius = 8 # working plane radius
global_epsilon = 0.000000001 # argument increment for derivative
centre = (global_epsilon, global_epsilon) # centre of the working circle
arr_shape = 100 # number of points processed / 360
step = radius / arr_shape # step between two points
def differentiable_function(x, y):
return np.sin(x) * np.exp((1 - np.cos(y)) ** 2) + \
np.cos(y) * np.exp((1 - np.sin(x)) ** 2) + (x - y) ** 2
def rotate_vector(length, a):
return length * np.cos(a), length * np.sin(a)
def derivative_x(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(global_epsilon + epsilon, arg) -
differentiable_function(epsilon, arg)) / global_epsilon
def derivative_y(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(arg, epsilon + global_epsilon) -
differentiable_function(arg, epsilon)) / global_epsilon
def calculate_flip_points():
flip_points = np.array([0, 0])
points = np.zeros((360, arr_shape), dtype=bool)
cx, cy = centre
for i in range(arr_shape):
for alpha in range(360):
x, y = rotate_vector(step, alpha)
x = x * i + cx
y = y * i + cy
points[alpha][i] = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x) > 0
if not points[alpha][i - 1] and points[alpha][i]:
flip_points = np.vstack((flip_points, np.array([alpha, i - 1])))
return flip_points
def pick_estimates(positions):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[1][0])
cx, cy = centre
best_x, best_y = cx + vx * positions[1][1], cy + vy * positions[1][1]
for index in range(2, len(positions)):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[index][0])
x, y = cx + vx * positions[index][1], cy + vy * positions[index][1]
if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y):
best_x = x
best_y = y
for index in range(360):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, index)
x, y = cx + vx * (arr_shape - 1), cy + vy * (arr_shape - 1)
if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y):
best_x = x
best_y = y
return best_x, best_y
def gradient_descent(best_estimates, is_x):
derivative = derivative_x if is_x else derivative_y
best_x, best_y = best_estimates
descent_step = step
value = derivative(best_y, best_x)
while abs(value) > global_epsilon:
descent_step *= 0.95
best_y = best_y - descent_step \
if derivative(best_y, best_x) > 0 else best_y + descent_step
value = derivative(best_y, best_x)
return best_y, best_x
def find_minimum():
return gradient_descent(gradient_descent(pick_estimates(calculate_flip_points()), False), True)
def get_grid(grid_step):
samples = np.arange(-radius, radius, grid_step)
x, y = np.meshgrid(samples, samples)
return x, y, differentiable_function(x, y)
def draw_chart(point, grid):
point_x, point_y, point_z = point
grid_x, grid_y, grid_z = grid
plot.rcParams.update({
'figure.figsize': (4, 4),
'figure.dpi': 200,
'xtick.labelsize': 4,
'ytick.labelsize': 4
})
ax = plot.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(point_x, point_y, point_z, color='red')
ax.plot_surface(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, rstride=5, cstride=5, alpha=0.7)
plot.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
min_x, min_y = find_minimum()
minimum = (min_x, min_y, differentiable_function(min_x, min_y))
draw_chart(minimum, get_grid(0.05))
===========
Источник:
habr.com
===========
Похожие новости:
- [Python, Машинное обучение, Искусственный интеллект, Natural Language Processing] Как сделать трансформер чат-бот на Trax?
- [Программирование, Совершенный код, C++, Лайфхаки для гиков] Прочти меня: код, который не выбесит соседа
- [Python, Обработка изображений] OpenCV в Python. Часть 4
- [Open source, Python, Параллельное программирование] Визуализируйте многопоточные программы Python с open source инструментом – VizTracer (перевод)
- [Python, *nix, C, Разработка под Linux] C и Python: мост между мирами
- [Python, Java, Разработка под Android, Искусственный интеллект, Flask] Играем с CLIP. Создаем универсальный zero-shot классификатор на Android
- [Python, Алгоритмы, 1С] Tesseract vs таблицы. Распознавание документов
- [Разработка веб-сайтов, Python, Django, Nginx] Запуск Django сайта на nginx + Gunicorn + SSL
- [Python, Работа с 3D-графикой, Разработка мобильных приложений] Кроссплатформенные OpenGL + Python при помощи Kivy
- [Python, Разработка под MacOS, Разработка под Linux, Разработка под Windows] Трепещущий Kivy. Обзор возможностей фреймворка Kivy и библиотеки KivyMD
Теги для поиска: #_python, #_gradientnyj_spusk (градиентный спуск), #_python, #_nahozhdenie_minimuma (Нахождение минимума), #_minimum_funktsii (Минимум функции), #_minimum (минимум), #_gradient (градиент), #_python
Вы не можете начинать темы
Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения
Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения
Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения
Вы не можете голосовать в опросах
Вы не можете прикреплять файлы к сообщениям
Вы не можете скачивать файлы
Текущее время: 14-Дек 17:57
Часовой пояс: UTC + 5
| Автор | Сообщение |
|---|---|
|
news_bot ®
Стаж: 7 лет 10 месяцев |
|
 Задача и требования
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot radius = 8 # working plane radius
centre = (global_epsilon, global_epsilon) # centre of the working circle arr_shape = 100 # number of points processed / 360 step = radius / arr_shape # step between two points def differentiable_function(x, y):
return np.sin(x) * np.exp((1 - np.cos(y)) ** 2) + \ np.cos(y) * np.exp((1 - np.sin(x)) ** 2) + (x - y) ** 2  Поскольку предел аргумента стремится к нулю, точность должна быть небольшой по сравнению с радиусом рабочей плоскости: global_epsilon = 0.000000001 # argument increment for derivative
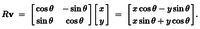 Если вращение применяется к вектору (x, 0), повернутый вектор будет вычисляться следующим образом: def rotate_vector(length, a):
return length * np.cos(a), length * np.sin(a) def derivative_y(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(arg, epsilon + global_epsilon) - differentiable_function(arg, epsilon)) / global_epsilon def derivative_x(epsilon, arg):
return (differentiable_function(global_epsilon + epsilon, arg) - differentiable_function(epsilon, arg)) / global_epsilon  Поскольку градиент вычисляется для 2D-функции, k равно нулю gradient = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x)
 Возвращаемое значение представляет собой массив приблизительных локальных минимумов.Локальный минимум распознается по смене знака производной с минуса на плюс. Подробнее об этом здесь: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxima_and_minima def calculate_flip_points():
flip_points = np.array([0, 0]) points = np.zeros((360, arr_shape), dtype=bool) cx, cy = centre for i in range(arr_shape): for alpha in range(360): x, y = rotate_vector(step, alpha) x = x * i + cx y = y * i + cy points[alpha][i] = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x) > 0 if not points[alpha][i - 1] and points[alpha][i]: flip_points = np.vstack((flip_points, np.array([alpha, i - 1]))) return flip_points def pick_estimates(positions):
vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[1][0]) cx, cy = centre best_x, best_y = cx + vx * positions[1][1], cy + vy * positions[1][1] for index in range(2, len(positions)): vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[index][0]) x, y = cx + vx * positions[index][1], cy + vy * positions[index][1] if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y): best_x = x best_y = y for index in range(360): vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, index) x, y = cx + vx * (arr_shape - 1), cy + vy * (arr_shape - 1) if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y): best_x = x best_y = y return best_x, best_y def gradient_descent(best_estimates, is_x):
derivative = derivative_x if is_x else derivative_y best_x, best_y = best_estimates descent_step = step value = derivative(best_y, best_x) while abs(value) > global_epsilon: descent_step *= 0.95 best_y = best_y - descent_step \ if derivative(best_y, best_x) > 0 else best_y + descent_step value = derivative(best_y, best_x) return best_y, best_x def find_minimum():
return gradient_descent(gradient_descent(pick_estimates(calculate_flip_points()), False), True) def get_grid(grid_step):
samples = np.arange(-radius, radius, grid_step) x, y = np.meshgrid(samples, samples) return x, y, differentiable_function(x, y) def draw_chart(point, grid):
point_x, point_y, point_z = point grid_x, grid_y, grid_z = grid plot.rcParams.update({ 'figure.figsize': (4, 4), 'figure.dpi': 200, 'xtick.labelsize': 4, 'ytick.labelsize': 4 }) ax = plot.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.scatter(point_x, point_y, point_z, color='red') ax.plot_surface(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, rstride=5, cstride=5, alpha=0.7) plot.show() if __name__ == '__main__':
min_x, min_y = find_minimum() minimum = (min_x, min_y, differentiable_function(min_x, min_y)) draw_chart(minimum, get_grid(0.05))  ЗаключениеПроцесс вычисления минимального значения с помощью алгоритма может быть не очень точным при вычислениях в более крупном масштабе, например, если радиус рабочей плоскости равен 1000, но он очень быстрый по сравнению с точным. Плюс в любом случае, если радиус большой, результат находится примерно в том положении, в котором он должен быть, поэтому разница не будет заметна на графике.Исходный код: import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot radius = 8 # working plane radius global_epsilon = 0.000000001 # argument increment for derivative centre = (global_epsilon, global_epsilon) # centre of the working circle arr_shape = 100 # number of points processed / 360 step = radius / arr_shape # step between two points def differentiable_function(x, y): return np.sin(x) * np.exp((1 - np.cos(y)) ** 2) + \ np.cos(y) * np.exp((1 - np.sin(x)) ** 2) + (x - y) ** 2 def rotate_vector(length, a): return length * np.cos(a), length * np.sin(a) def derivative_x(epsilon, arg): return (differentiable_function(global_epsilon + epsilon, arg) - differentiable_function(epsilon, arg)) / global_epsilon def derivative_y(epsilon, arg): return (differentiable_function(arg, epsilon + global_epsilon) - differentiable_function(arg, epsilon)) / global_epsilon def calculate_flip_points(): flip_points = np.array([0, 0]) points = np.zeros((360, arr_shape), dtype=bool) cx, cy = centre for i in range(arr_shape): for alpha in range(360): x, y = rotate_vector(step, alpha) x = x * i + cx y = y * i + cy points[alpha][i] = derivative_x(x, y) + derivative_y(y, x) > 0 if not points[alpha][i - 1] and points[alpha][i]: flip_points = np.vstack((flip_points, np.array([alpha, i - 1]))) return flip_points def pick_estimates(positions): vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[1][0]) cx, cy = centre best_x, best_y = cx + vx * positions[1][1], cy + vy * positions[1][1] for index in range(2, len(positions)): vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, positions[index][0]) x, y = cx + vx * positions[index][1], cy + vy * positions[index][1] if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y): best_x = x best_y = y for index in range(360): vx, vy = rotate_vector(step, index) x, y = cx + vx * (arr_shape - 1), cy + vy * (arr_shape - 1) if differentiable_function(best_x, best_y) > differentiable_function(x, y): best_x = x best_y = y return best_x, best_y def gradient_descent(best_estimates, is_x): derivative = derivative_x if is_x else derivative_y best_x, best_y = best_estimates descent_step = step value = derivative(best_y, best_x) while abs(value) > global_epsilon: descent_step *= 0.95 best_y = best_y - descent_step \ if derivative(best_y, best_x) > 0 else best_y + descent_step value = derivative(best_y, best_x) return best_y, best_x def find_minimum(): return gradient_descent(gradient_descent(pick_estimates(calculate_flip_points()), False), True) def get_grid(grid_step): samples = np.arange(-radius, radius, grid_step) x, y = np.meshgrid(samples, samples) return x, y, differentiable_function(x, y) def draw_chart(point, grid): point_x, point_y, point_z = point grid_x, grid_y, grid_z = grid plot.rcParams.update({ 'figure.figsize': (4, 4), 'figure.dpi': 200, 'xtick.labelsize': 4, 'ytick.labelsize': 4 }) ax = plot.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.scatter(point_x, point_y, point_z, color='red') ax.plot_surface(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, rstride=5, cstride=5, alpha=0.7) plot.show() if __name__ == '__main__': min_x, min_y = find_minimum() minimum = (min_x, min_y, differentiable_function(min_x, min_y)) draw_chart(minimum, get_grid(0.05)) =========== Источник: habr.com =========== Похожие новости:
|
|
Вы не можете начинать темы
Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения
Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения
Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения
Вы не можете голосовать в опросах
Вы не можете прикреплять файлы к сообщениям
Вы не можете скачивать файлы
Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения
Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения
Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения
Вы не можете голосовать в опросах
Вы не можете прикреплять файлы к сообщениям
Вы не можете скачивать файлы
Текущее время: 14-Дек 17:57
Часовой пояс: UTC + 5
